Thermal Spraying
Flame Wire Spraying
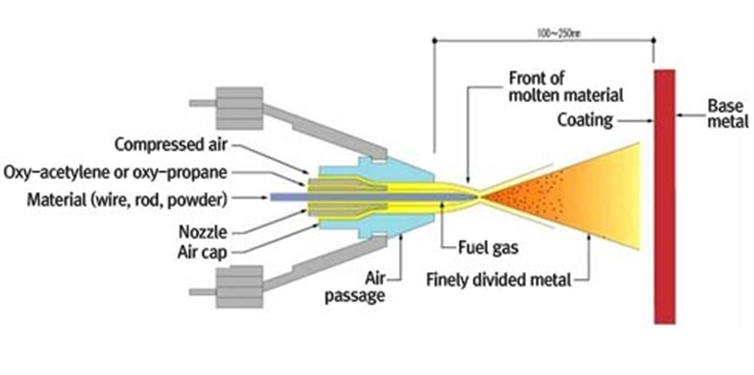
- Flame Wire Spraying Overview
- In flame wire spraying, a typical gas spraying method, wires are consecutively fed into a gas flame, such as oxy-acetylene or oxy-propane, get molten and sprayed using compressed air to form coatings. All kinds of metals that can be made into wires, including zinc, aluminum, carbon steel, stainless steel, and molybdenum, can be applied to the spraying technique. Thickness range is wids, from 0.1 up to 10 micrometers.
- Characteristics
- Using lightweight equipment, suitable for on-site construction
- Little to not thermal distortion of base metals
- Adjustable thickness range(01.~10 micrometers)
- A wide choice of materials
- High wear resistance of coatings
Arc Spraying
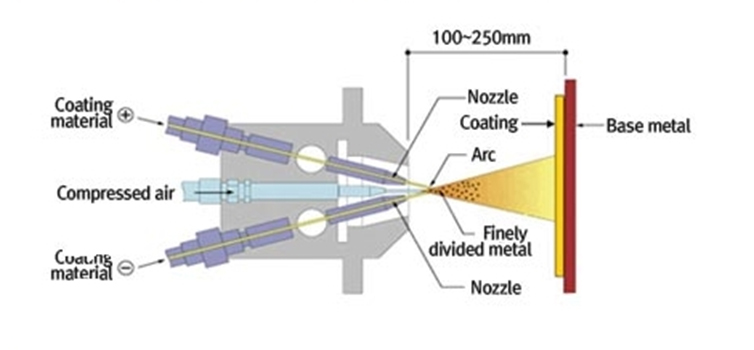
- Arc Spraying Overview
- In this typical electric spraying, tow metal wires generate electrical arc discharge and get molten and fed in keeping pace with the melting velocity. The melted metals then get finally divided by compressed air and consecutively molded on a bse metal, forming a coating. Compared with the flame spraying methods, it shows excellent performance. Since a coating material can be thoroughly molten high temperature, it provides outstanding adhesion to a base materials. However, coating materails are limited to those electrically conductive.
- Characteristics
- Fast spraying(two to four times faster than flamed spraying)
- High adhesive strength and coating strength
- Using different types of materials, can form alloy coating
- Low operating costs
HVOF Flame Spraying
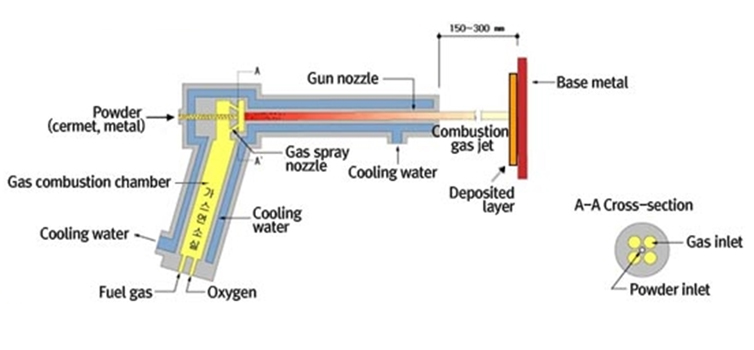
- HVOF Flame Spraying Overview
- This methods forms coatings by using powerful spray impact genrated by the increased spray velocity. Using the same fuel gas as flame spraying, it is divided into HVOF(High Velocity Oxy-Fuel) using a mixture of fuel and oxygen and HVAF(High Velocity Air-Fuel) using a mixture of fuel and air. It works under the principle that 1) combustion occurs inside a tube; 2) a combustion gas is sprayed at high velocity through a nozzle; 3) powder is fed into the sparyed gas and gets heated, molten, and sprayed at high velocity, finally forming a coating.
- Characteristics
- Two or four times faster than spraying
- Can form delicate coatings
- Oxidation occurs less
- Requires finer powders
- Can cause clogging in the spray gun
- Generates ultrasound-Work needs to get done inside an isolated soundproof room
Plasma Spraying
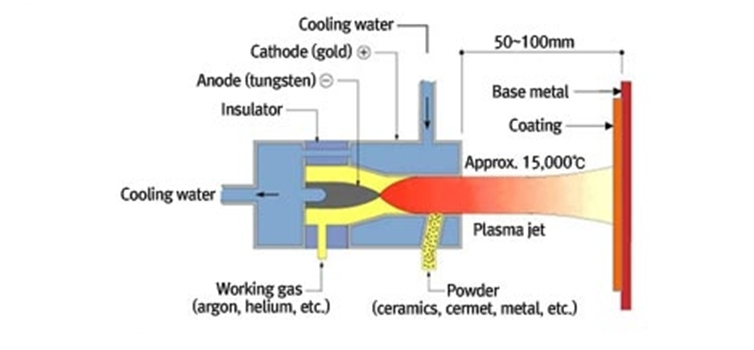
- Plasma Spraying Overview
- In plasma spraying using a high temperature, high-velocity plasma jet generated by arc discharge in argon, powder materials ared fed, molten, and accelerated to result in coatings. With high energy density, the plasma jet helps achieve temperatures higher than 10,000℃, allowing the spraying of almost every material, including metals with high melting points, cermets, and ceramics. depending upon the coating material, the plasma jet offers a wide choice of temperatures, increasing the degree of freedom of coating materials and improving adherence to base metals and spray coatings.
- Characteristics
- High melting temperatures allow ceramic spraying(2,000 ~ 32,000K)
- A wide choice of coating materials
- Allows spraying in inactive of decompression chambers
- Forming high-density coatings, excellent adherence to base metals
Head Office in Gumi Address : (39422) 39 4gongdan-ro 7-gil, Gumi-si, Gyeongsangbuk-do
Tel : 054-473-8968~70 Fax : 054-471-4781 Email : kstgumi@kst1.co.kr COPYRIGHT (C) 2013 KOREA STAR TECH CO,.LTD. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.
Tel : 054-473-8968~70 Fax : 054-471-4781 Email : kstgumi@kst1.co.kr COPYRIGHT (C) 2013 KOREA STAR TECH CO,.LTD. ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.